TUESDAY TECH BYTES - Adobe Campaign Classic

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
Hello Adobe Campaign Community!
Welcome to 'Tuesday Tech Bytes' series, a weekly discussion on exploring a wide range of valuable topics such as best practices, integrations, success stories and hidden gems.
Tune in every Tuesday for a new discussion!
Theme 1 - ACC Tips & Tricks
Theme 2 - ACC Best Practices
Theme 3 - ACC Integrations
Theme 4 - ACC Golden Nuggets.
We are absolutely thrilled to embark on this journey of learning and growth with all of you and We warmly invite you to engage with our posts by liking, commenting, and sharing!
Quick Links:
- Keep interim results and Log SQL Journal
- Variables
- Best Practices: Workflow
- Best Practices: Schema
- Adobe Target Integration
- Snowflake Integration
- Cardinality
- Exploring 'Query'
Thanks @Jagpreet_Singh_ for this initiative!
Feel free to visit other communities where SME's will be posting useful bytes in their respective tool!
Tuesday Tech Byte Links:
|
Author: @ParthaSarathy |
|
|
Author: @Darshil_Shah1 |
|
|
Author: @aanchal-sikka and @Anmol_Bhardwaj |
|
|
Author: @Benjienen |
|
|
Author: @Madalyn_Destafney |
|
|
Author: @PratheepArunRaj |
|
|
Author: @Gokul_Agiwal and @Rajneesh_Gautam_ |
Topics help categorize Community content and increase your ability to discover relevant content.

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
💡 Tips & Tricks 💡
Keep interim populations
The 'Keep the result of interim populations between two executions' option keeps temporary tables between two executions of a workflow.
This option in workflow property’s General tab can be used for development and test purpose to monitor data and check results. You can use this option in development environments, but Never use it on production environments.
This option consumes a lot of disk space⚠️.
Keeping temporary tables could result in the size of the database increasing significantly and eventually the size limit being reached.
THIS OPTION MUST NEVER BE CHECKED IN A PRODUCTION WORKFLOW.
There might be many scenarios where a developer may enable this 'Keep interim populations' checkbox during development or testing phase, but might get forget to uncheck it. If there are many workflows in your instance with this option enabled, it will lead to consume a lot of disk space.
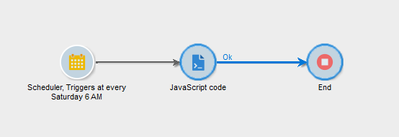
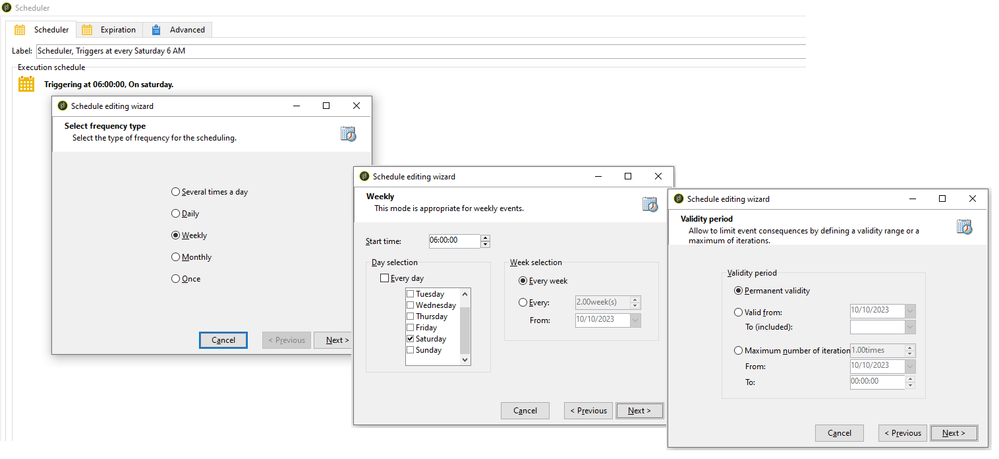
To avoid it, you can create a technical workflow as below to automatically uncheck the 'Keep interim populations' option.
SCHEDULER
Schedule the workflow to run once a week.
JavaScript
Below script will fetch all the workflows which have been modified 7 days before with 'Keep the result of interim populations between two executions' option enabled and update the keep interim flag as 'false', which will uncheck this option in workflow property.
var sevenDaysAgo = new Date();
sevenDaysAgo.setDate(sevenDaysAgo.getDate() - 7);
sevenDaysAgo = formatDate(sevenDaysAgo, "%2M/%2D/%4Y %2H:%2N:%2S");
var query = xtk.queryDef.create(
<queryDef schema="xtk:workflow" operation="select">
<select>
<node expr="@id"/>
<node expr="@lastModified"/>
<node expr="@keepResult"/>
</select>
<where>
<condition expr={"@lastModified <'"+ sevenDaysAgo +"'"}/>
</where>
</queryDef>
);
var record = query.ExecuteQuery();
for each (var variable in record) {
if(variable.@keepResult == true){
var primaryKey = variable.@id;
var keepInterimResult = 0;
xtk.session.Write(<workflow xtkschema="xtk:workflow" _operation="update" id={primaryKey} keepResult={keepInterimResult} />);
}
}Note:
- Try the above workflow in your lower environments before running it in PRODUCTION.
- Recommend the Operators to NOT to enable keep interim flag in PROD.

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
Nice initiative @ParthaSarathy @Jagpreet_Singh_
I have a similar workflow where I also add a piece to remove SQL Log in case it was also check.
will be happy to share the package if needed.
Thanks,
David
David Kangni


- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
Thank you @DavidKangni .
Yes Sure, kindly share the workflow package. It will be an additional learning for us!!

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
PFA,
check and let me know. During import, you may need to update console build.
Thanks,
David
David Kangni


- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
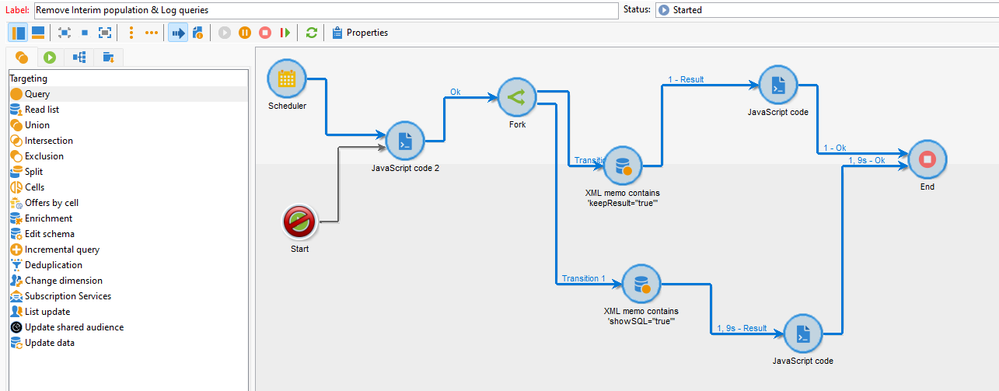
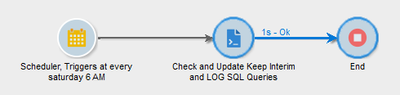
Thanks @DavidKangni for the package, I will have a look at it.
From the above script, I have added few lines of script to check and update 'Log SQL queries in the journal' along with keep interim results.
var sevenDaysAgo = new Date();
sevenDaysAgo.setDate(sevenDaysAgo.getDate() - 7);
sevenDaysAgo = formatDate(sevenDaysAgo, "%2M/%2D/%4Y %2H:%2N:%2S");
var query = xtk.queryDef.create(
<queryDef schema="xtk:workflow" operation="select">
<select>
<node expr="@id"/>
<node expr="@lastModified"/>
<node expr="@keepResult"/>
<node expr="@showSQL"/>
</select>
<where>
<condition expr={"@lastModified <'"+ sevenDaysAgo +"'"}/>
</where>
</queryDef>
);
var record = query.ExecuteQuery();
for each (var variable in record) {
if(variable.@keepResult == true){
var primaryKey = variable.@id;
var keepInterimResult = 0;
xtk.session.Write(<workflow xtkschema="xtk:workflow" _operation="update" id={primaryKey} keepResult={keepInterimResult} />);
}
if(variable.@showSQL == true){
var primaryKey = variable.@id;
var showSqlLogs = 0;
xtk.session.Write(<workflow xtkschema="xtk:workflow" _operation="update" id={primaryKey} showSQL={showSqlLogs} />);
}
}
- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
This is great, thank you for sharing! We regularly see our DB usage spike due to Keep Interim, so this automation will come in really handy.
Saying that, we find that the reality is that Keep Interim is a necessary evil, in order to validate, reconcile and debug live campaigns. The directive to "not use in Production" would be more powerful if there was some alternative way to achieve what our Campaign Developers need to achieve.
![]()
- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
There should be an option to "Keep Sample Population" where users can see a only a subset of the data. Just a thought
Views
Replies
Total Likes

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
Tips & Tricks
VARIABLES
Task Variable
A Task Variable created in an activity can be used only by the current task/activity. Example, If a task variable is created in Query activity's Advanced tab > Initialization script, then the value stored in this task variable will be applicable only within this Query activity, and if this task variable is called in another Activity of the same workflow, it will populate result as 'undefined'.
Syntax: task.vars.xxx
Event Variable
An event variable created in an activity can be passed to the following activities.
Syntax: vars.xxx
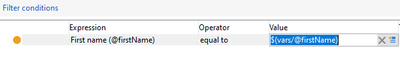
Using Event Variable in filtering Condition:
Consider an Event variable is created in beginning of the workflow as vars.firstName='Partha';
In Query to filter First name equals to vars.firstName, refer the Event variable in the Value column as $(vars/@firstName).
Instance Variable
The instance variables are comparable to global variables. They are shared by all activities in the same workflow.
Syntax: instance.vars.xxx
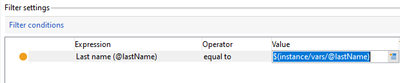
Using Instance Variable in filtering Condition:
Consider an Instance variable is created in beginning of the workflow as instance.vars.lastName='Sarathy';
In Query to filter Last name equals to instance.vars.lastName, refer the Instance variable in the Value column as $(instance/vars/@lastName).
Event Variable Vs Instance Variable
In the below Workflow there are 2 independent flows.
Consider an Event variable is created in JS-1 on 1st flow. In the same flow, it is possible to read the value of JS-1's event variable in JS-2.
But when it is tried to call the 1st flow's event variable in 2nd flow (say, JS-3), it will print 'undefined'.
So, If the requirement is to create a variable in JS-1, which can also be used in JS-3 (another flow of same workflow), then create it as instance variable.
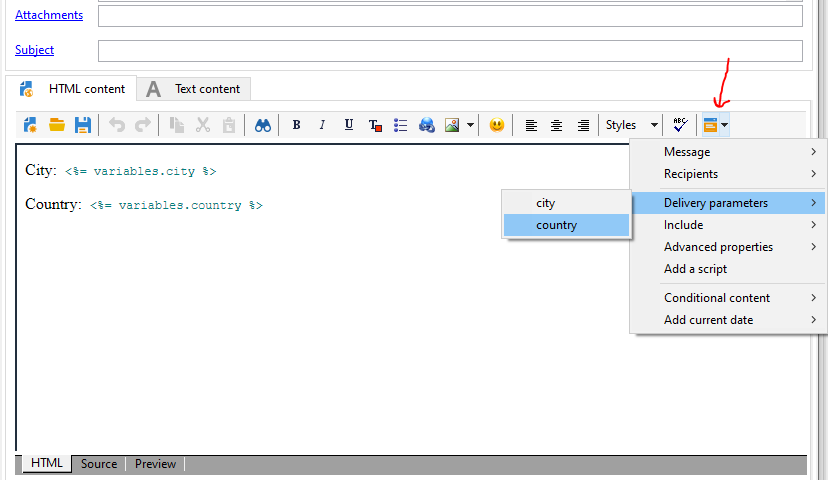
Calling a Variable in the Content of the Delivery
Few Requirement requires to call these event variable or instance variable inside the delivery content or in the delivery attachments. In such cases, we need to make few configurations as below to populate the event variable / instance variable of a workflow inside the delivery content.
Consider 2 instance variables are created in the workflow,
instance.vars.city = 'Chennai';
instance.vars.country = 'India';
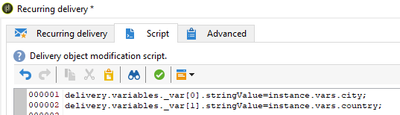
To call these instance variable inside the delivery content, In Delivery's Script tab (Right click delivery activity > Open), and add instance variable to delivery.variables as below,
delivery.variables._var[0].stringValue=instance.vars.city;
delivery.variables._var[1].stringValue=instance.vars.country;
(If there are many variables, add another lines with incrementing var[2] var[3] etc.,)
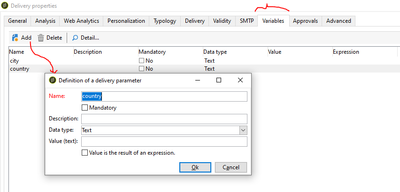
Now navigate to delivery properties' Variable tab.
Add > Name: city > ok
Add > Name: country > ok
In Delivery Body > include dropdown > Delivery Parameters > All the variables created in the properties will be visible here
Now <%= variables.city %> will populate the value of instance.vars.city and <%= variables.country %> populate the value of instance.vars.country

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
Hello @ParthaSarathy;
Thank you for your initiative.
i wanted to add some tips that permit to force the type of the variable in the query :
- $string(vars/@myVar) to force the type of your variable as string
- $long(vars/@myVar) to force the type of your variable to be a long
- $int64(vars/@myVar) to force the type of your variable to be an int64
- $date(vars/@myVar) to force the type of your varibale to be a date
- $datetime(vars/@myVar) to force the type of your varibale to be a datetime
- $noescaping(vars/@myVar) (the one I use the most) deactivates the escaping.
I use it when I have a need to use the 'IN' or 'NOT IN' operator in my query.
Let's say vars/@myVar = 'A','B','D'. If I do "@col IN $(vars/@myVar)" in Adobe, it translates it as "@col IN (''A','B','D'')" which doesn't work :/.
With $noescaping, the quotes aren't added, and the query works just fine.
Br,
Amine

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
BEST PRACTICE
Workflow Best Practices:
- Try to maintain a stable level of activity along the day and avoid peaks to prevent the instance from overload. To do so, distribute workflow starting times evenly throughout the day.
- Long workflows can potentially have an impact on the server and database resources. Split the longest workflows to reduce processing time.
- To reduce overall run times, replace time-consuming activities with simplified and faster activities.
- Avoid running more than 20 workflows simultaneously. When too many workflows are executed at the same time, the system can run out of resources and become unstable.
- Disable 'Keep the result of interim populations between two executions' and 'Log SQL queries in the journal' in workflow property
These are few best practices to keep in mind when building a workflow. Please feel free to comment and share other workflow best practices!

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
Best Practices
There many online Best Practices documentation available to create a healthy campaign Environment. Here are the few highlighting Best Practices for this week,
- Do no try to schedule large deliveries together. There is a gap of 5-10 minutes to spread the load uniformly over the system. Coordinate the scheduling of deliveries with the other members of your team to ensure the best performance. When the marketing server is handling many different tasks at the same time, it can slow down performance.
- Keep the size of your emails as low as possible. The recommended maximum size of an email is about 35KB. The size of an email delivery generates a certain amount of volume in the sending servers.
- Large deliveries, such as deliveries to over one million recipients, need space in the sending queues. This alone is not an issue for the server, but when combined with dozens of other large deliveries all going out at the same time, it can introduce a sending delay.
- When creating additional custom recipient tables, make sure you have a dedicated log table for each delivery mapping.
- Reduce the days as much as you can the depth of log retention.
- To prevent any performance issue related to the high number of rows, only keep the necessary records in the database. Any other record should be exported to a third-party data warehouse and removed from the Adobe Campaign operational database.
- When creating large tables, create it with fewer fields / columns. And do not use large number type of column (ex: Int64) to store small numbers like Boolean values.

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
ADOBE TARGET INTEGRATION
Adobe campaign classic and Adobe Target Integration
Adobe campaign classic can be integrated with Adobe Target to optimize email content with personalized dynamic images.
For example, we can display different offer images for different recipients based on Recipient's Country.
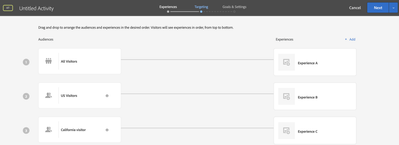
In Adobe Target, Create a Experience targeting activity as below and publish it,
country equals to India >> Experience A
country equals to United States >> Experience B
All Visitors >> Experience C
Prerequisites:
Collect the below details from Adobe Target,
- Adobe Target's Domain Server details
- Client Code (To get client code, Adobe target > setup > implementation > implementation method: Edit Settings > Advanced Settings: Client code)
- Rawbox
- AT Property
- Decision parameter name (In our example, decision parameter name is 'country')
Now in Adobe Campaign Classic, Install the Integration with the Adobe Experience Cloud built-in package (Tools > Advanced > Import Package > Install a standard package > Select 'Integration with the Adobe Experience Cloud' > Start)
Next, Navigate to Administration > Platform > Options > search for the below options and configure the values.
1) TNT_EdgeServer - Enter Adobe Target's Domain Server details in value textbox.
2) TNT_TenantName - Enter Adobe Target's client code.
Create a New Email Delivery.
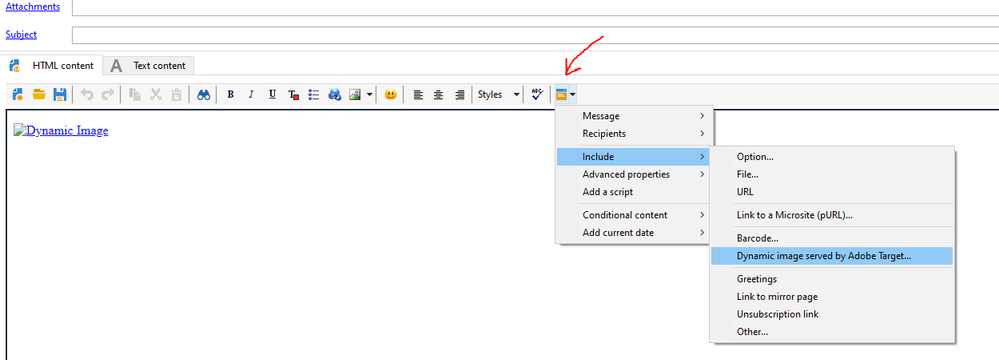
HTML Content > include > dynamic image served by Adobe target
Default image: URL of an image (Default image will be rendered to Recipients who does not belongs to any Experience created in Adobe Target)
Target location (Rawbox): Paste the rawbox detail collected from Adobe Target
Landing Page: URL of a Landing page when user click on the image
Target Property: Paste the AT Property detail collected from Adobe Target
Additional decision parameter:
Name - country
Select - recipient.country.label
When the delivery is triggered, each recipient will be receiving an email with the personalized image based on their country.

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
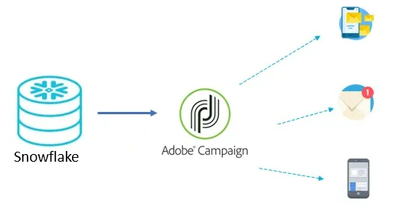
SNOWFLAKE INTEGRATION
The Snowflake and Adobe Campaign (V7) integration provides users with the ability to unlock deep value from their data by offering a single, unified, and easy-to-use platform for data analysis. Snowflake equips organizations with a single, integrated platform that offers the data warehouse built for the cloud; instant, secure and governed access to their entire network of data; and a core architecture to enable many types of data workloads, including a single platform for developing modern data applications.
Click here To know more...
Prerequisites:
To Integrate Adobe campaign classic with Snowflake, Get the following details from SNOWFLAKE
- Snowflake Server URL
- Name of the user
- Password
- Role and Warehouse (Name of the default warehouse to use)
- Database (Snowflake database, where the workflow's temporary table needs to be created)
- Schema (Database schema to use for work tables)
Remote database access rights:
To process the data contained in an external database, the Adobe Campaign user must have at least ‘Write’ rights on the database to be able to create worktables. These are deleted automatically by Adobe Campaign.
Generally, The following rights are necessary:
- CONNECT: connection to the remote database
- READ Data: read-only access to tables containing customer data
- READ ‘MetaData’: access to the server data catalogs to obtain the table structure
- LOAD: mass loading in work tables (required when working on collections and joins)
- CREATE/DROP for TABLE/INDEX/PROCEDURE/FUNCTION (only for worktables generated by Adobe Campaign)
- EXPLAIN (recommended): for monitoring performances in case of problems
- WRITE Data (depending on the integration scenario).
Adobe Campaign:
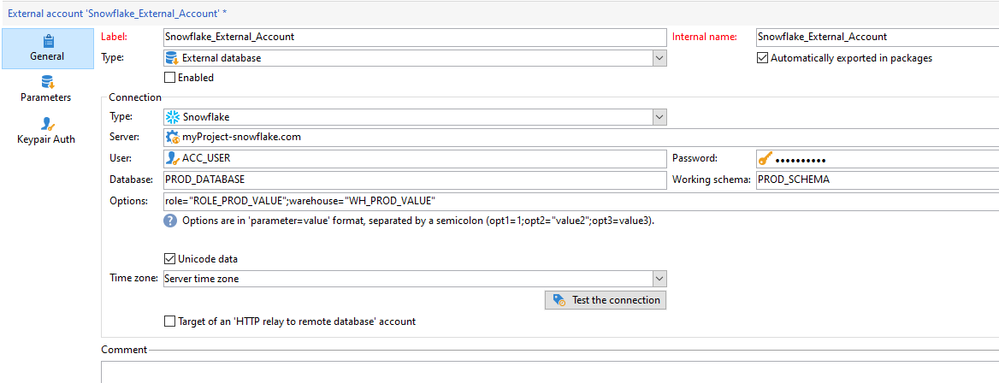
> Navigate to /Administration/Platform/External Accounts/
> Create new external account.
> In General tab,
- Provide the Label and internal name: Snowflake_External_Account
- Type: External database
CONNECTION:
- Type: Snowflake
- Server:
- User:
- Password:
- Database:
- Working Schema:
- Options: Enter the role and warehouse details in below format:
role="ROLE_PROD_VALUE";warehouse="WH_PROD_VALUE"> Save the External account and 'Test the connection'.
In Parameters tab, Click on Deploy functions button to create functions.
For Keypair authentication, click the Keypair Auth tab to use your Private key to authenticate and copy paste your Private key.
DATA SCHEMA:
To extend the TABLES and VIEWS from snowflake, Navigate to /Administration/Configuration/Data schemas/
New > Access External Data > Select the external account 'Snowflake_External_Account' > and from Tables, Select the table to be extended >
Next > The schema structure will get auto-generated > Save it.
- Data type, label, name, length and sqlname will get auto-generated. If required< modify the data type, label, name and length and Do Not modify sqlname of it.
- Define primary key, dbindex and cardinality manually.
- Not required to update the database structure.
In Data tab, we can preview the data from snowflake.

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
CARDINALITY
A link describes the association between one table and another.
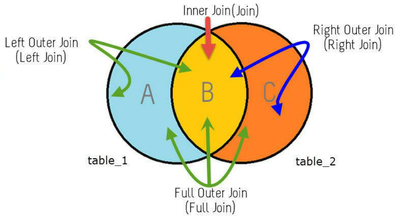
The various types of associations (known as “cardinalities”) are as follows:
- Cardinality 1-N (1 to Many)
- Cardinality 1-1 (Left Join, Right Join, Inner Join, Outer Join)
- Cardinality N-N
Lets discuss about Basic syntax for various link definitions.
1 to Many
WHEN: one occurrence of the source table can have several corresponding occurrences of the target table, but one occurrence of the target table can have at most one corresponding occurrence of the source table.
Example: nms:recipient and nms:broadLogRcp schema
Where 1 Recipient can have multiple records in BroadLogRcp schema and 1 BroadLogRcp can be linked with only one Recipient record.
WHERE: Where to code the 1 to N link Definition?
In 1 to Many cardinality, the code should be written in Target (Many-N) schema. In the above example, the code should be written in nms:broadLogRcp schema.
Basic Syntax:
<element label="Recipient" name="recipient" revLabel="Recipient delivery logs" target="nms:recipient" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@destination_key_attribute" xpath-src="@source_key_attribute"/>
</element>
1 to 1
One occurrence of the source table can have at most one corresponding occurrence of the target table.
With the same syntax of 1 to Many join, add revCardinality="single" to make it as 1 to 1 Join.
We will explore how to write syntax for 1-1 Left join, Right join, Inner join and Outer Join.
WHERE: Where to write the script?
We can write the link definition in any of the schema. For the below example, consider the script is written in 'Table_1'
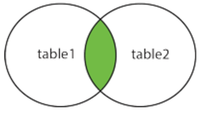
1 to 1 Inner Join
By default syntax of 1 to 1 Join, the cardinality will act as 1 to 1 inner join.
<element revCardinality="single" label="Target Schema Label" name="target_Schema_name" revLabel="Source Schema Label" target="abc:targetSchema" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@destination_key_attribute" xpath-src="@source_key_attribute"/>
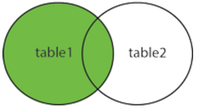
</element>1 to 1 Left Join
With the 1 to 1 link definition syntax, add externalJoin="true" to it.
<!-- Script is written in table_1 -->
<element externalJoin="true" revCardinality="single" label="Target Schema Label" name="target_Schema_name" revLabel="Source Schema Label" target="abc:targetSchema" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@destination_key_attribute" xpath-src="@source_key_attribute"/>
</element>1 to 1 Right Join
With the 1 to 1 link definition syntax, add revExternalJoin="true" to it.
<!-- Script is written in table_1 -->
<element revExternalJoin="true" revCardinality="single" label="Target Schema Label" name="target_Schema_name" revLabel="Source Schema Label" target="abc:targetSchema" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@destination_key_attribute" xpath-src="@source_key_attribute"/>
</element>1 to 1 Full Outer Join
Add both externalJoin="true" and revExternalJoin="true" to the 1 to 1 syntax as below,
<!-- Script is written in table_1 -->
<element externalJoin="true" revExternalJoin="true" revCardinality="single" label="Target Schema Label" name="target_Schema_name" revLabel="Source Schema Label" target="abc:targetSchema" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@destination_key_attribute" xpath-src="@source_key_attribute"/>
</element>
Many to Many
Many to Many (N - N) - one occurrence of the source table can have several corresponding occurrences of the target table, and vice-versa.
In Adobe Campaign, to create Many to many link between two schema, we have to create an relationship (intermediate) table. A relationship table will be linked 1:N with each table and this will let you link two tables with cardinality N-N.
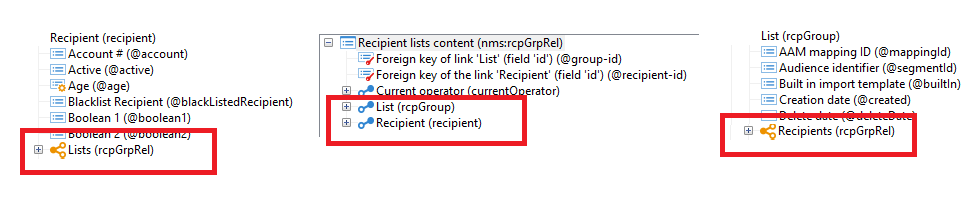
Example: One Recipient can have multiple records in List and one List can store multiple Recipients in it.
So, to create many to many relationship with nms:recipient and nms:group schema, there is an OOTB relationship (intermediate) table 'Recipient lists content' (nms:rcpGrpRel)
nms:rcpGrpRel Table has 2 attributes as composite primary key: group-id and recipient-id.
In this intermediate relationship table, Link will be created as 1 rcpGrpRel can have multiple Recipients( 1 to Many) and 1 rcpGrpRel can have multiple Lists ( 1 to Many)
<element label="Recipient" name="recipient" target="nms:recipient" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@id" xpath-src="@recipient-id"/>
</element>
<element label="List" name="rcpGroup" target="nms:group" type="link">
<join xpath-dst="@id" xpath-src="@group-id"/>
</element>Based on the requirement of the cardinality, the following optional attributes can be added along with basic syntax,
-
revLink (optional): name of reverse link from the target schema (deduced automatically by default),
-
integrity (optional): referential integrity of the occurrence of the source table to the occurrence of the target table. Possible values are as follows:
- define: it is possible to delete the source occurrence if it is no longer referenced by a target occurrence,
- normal: deleting the source occurrence initializes the keys of the link to the target occurrence (default mode), this type of integrity initializes all foreign keys,
- own: deleting the source occurrence leads to the deletion of the target occurrence,
- owncopy: the same as own (in case of deletion) or duplicates the occurrences (in case of duplication),
- neutral: does nothing.
-
revIntegrity (optional): integrity on the target schema (optional, “normal” by default)

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
@ParthaSarathy Very good stuff, keep it up.

- Mark as New
- Follow
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report
QUERY
Targeting Dimension & Filtering Dimension
The targeting dimension lets you define the population targeted by the operation
Frequently used query conditions
The filtering dimension lets you select the population based on certain criteria
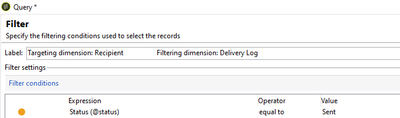
For Example, to select recipients who received a particular email, select the targeting dimension as Recipients schema and the filtering dimension as Delivery Logs Schema.
Alternatively, In the above example, we can also have both targeting dimension and filtering dimension as Recipient schema, and inside filtering condition expression we can use Delivery Log exists such as as below,
In queries, “exists such as” conditions in filters are not efficient. They are the equivalent of a sub-query in SQL
Instead, As a BEST PRACTICE, Select targeting dimension as Recipient and Filtering dimension as Delivery Log Schema, in filtering condition expression, you can find attributes of Delivery Log schema and directly use those attributes. The equivalent of the filtering dimension in SQL is the inner join:
SQL statement comparison for the above 2 screenshot query conditions,
Exist such as:
SELECT DISTINCT R0.iRecipientId FROM NmsRecipient R0 WHERE EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM NmsBroadLogRcp B1 WHERE (B1.iRecipientId = R0.iRecipientId) AND (((B1.iStatus = 1)))) AND ((R0.iRecipientId > 0 OR R0.iRecipientId < 0))
Selecting Filtering Dimension:
SELECT DISTINCT R1.iRecipientId FROM NmsBroadLogRcp B0 JOIN NmsRecipient R1 ON (R1.iRecipientId = B0.iRecipientId) WHERE (B0.iStatus = 1) AND ((B0.iBroadLogId > 0 OR B0.iBroadLogId < 0))
Query Conditions
With 1 to Many linked schema, 4 different operators can be seen in Query editor and Lets discuss about it with few examples,
Example: To fetch recipients who have Received a particular email But haven't opened it.
Targeting Dimension: nms:recipient
Fileting Dimension: nms:recipient
Exist: To fetch recipients who have at least one record in its linked schema.
For example, There is a 'Complaint' schema, where whenever a recipient has raised a complaint request, a record will get created in Complaint schema linked with recipient (1 to Many link between recipient and complaint schema)
Targeting Dimension: nms:recipient
Fileting Dimension: nms:recipient
Select Complaint schema from Expression and operator as 'Exist'.
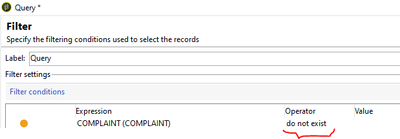
Do not exist: To fetch recipients who have NO record in its linked schema.
In the same above example of 'Complaint' schema, where a recipient has not raised a single complaint request.
Targeting Dimension: nms:recipient
Fileting Dimension: nms:recipient
Select Complaint schema from Expression and operator as 'Do not Exist'.
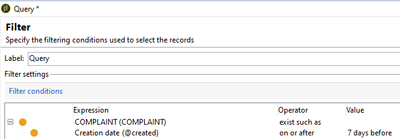
Exist such as: To fetch recipients who have at least one record in its linked schema and satisfying particular additional condition in its linked schema.
Example, In 'Complaint' schema, to fetch recipient who has raised a complaint request in last 7 days.
Targeting Dimension: nms:recipient
Fileting Dimension: nms:recipient
Select Complaint schema from Expression and operator as 'Exist such as' and in sub-condition, creation date on or after DaysAgo(7)
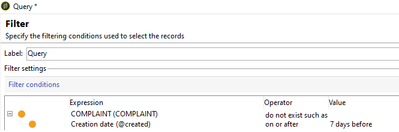
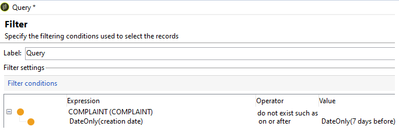
Do not exist such as: To fetch recipients who have NO records in its linked schema and satisfying particular additional condition in its linked schema.
Example, To fetch recipient who haven't raised a complaint request in last 7 days.
Targeting Dimension: nms:recipient
Fileting Dimension: nms:recipient
Select Complaint schema from Expression and operator as 'Do not Exist such as' and in sub-condition, creation date on or after DaysAgo(7)
Additionally, when the Date time field like creation date is used in query conditioned and value is mentioned as DaysAgo(7), be aware that it will be considering the time as well. Example, if the workflow runs at 28/10/2023 18:21:00, then DaysAgo(7) will fetch records created from 21/10/2023 18:21:00
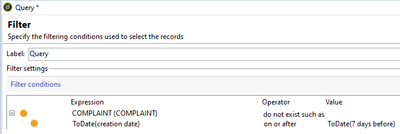
But, If the logic requires to fetch all the records created 7 days ago irrespective of time (From 12 AM), either use ToDate() function on both expression and value
Example,
ToDate(@created) on or after ToDate(DaysAgo(7))
Or use DateOnly() function on both expression and value
DateOnly(@created) on or after DateOnly(DaysAgo(7))
So either by using ToDate() or DateOnly() function, if the workflow runs at 28/10/2023 18:21:00, then DaysAgo(7) will fetch all the records created from 21/10/2023 00:00:00
To know more about other list of available functions, Refer this link.
Views
Likes
Replies
Views
Likes
Replies
Views
Likes
Replies