Creation of Content Fragments through Rest client (Postman)

Creation of Content Fragments through Rest client (Postman)
by <Sivakumar Kanoori>Overview
Creation of Content Fragments through Rest client (Postman)
Adobe Experience Manager (AEM) Content Fragments are text-based editorial content that may include some structured data elements associated but considered pure content without design or layout information. Content Fragments are typically created as channel-agnostic content, that is intended to be used and re-used across channels, which in turn wrap the content in a context-specific experience.
Content Fragments, independent of layout, can be used directly in AEM Sites with Core Components or can be delivered in a headless manner to downstream channels.
- Using Content Fragments on web pages
- Exposing Content Fragments as JSON using AEM Content Services
Manual Creation of content fragments :
Here, we can see how we can create the content fragments using existing Models through rest client :
- Develop the AEM Servlet : It Should be Post.
@component(service = { Servlet.class }, property = { “sling.servlet.paths=/bin/cfCreation”,“sling.servlet.methods=” + HttpConstants.METHOD_POST })
public class ContentFragmentCreationServlet extends SlingAllMethodsServlet
{
public void doPost(SlingHttpServletRequest request, SlingHttpServletResponse response) {
JsonElement createParams = null;
createParams = getPayloadFromRequest(request);
ResourceResolver resolver = request.getResourceResolver();
}
private JsonElement getPayloadFromRequest(SlingHttpServletRequest request) throws InvalidParameterException {
try (BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(request.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
String requestParams = br.lines().collect(Collectors.joining());
return new Gson().getAdapter(JsonElement.class).fromJson(new StringReader(requestParams));
} catch (IOException exc) {
LOG.error("Error Reading input Parameters", exc);
throw new InvalidParameterException("Failed to read parameters from request");
} catch (JsonSyntaxException exc) {
LOG.error("Error Reading input Parameters: invalid json");
throw new InvalidParameterException("Invalid json");
}
}
}
@8220494(service = { Servlet.class }, property = { “sling.servlet.paths=/bin/cfCreation”,“sling.servlet.methods=” + HttpConstants.METHOD_POST })
public class ContentFragmentCreationServlet extends SlingAllMethodsServlet
public void doPost(SlingHttpServletRequest request, SlingHttpServletResponse response) {
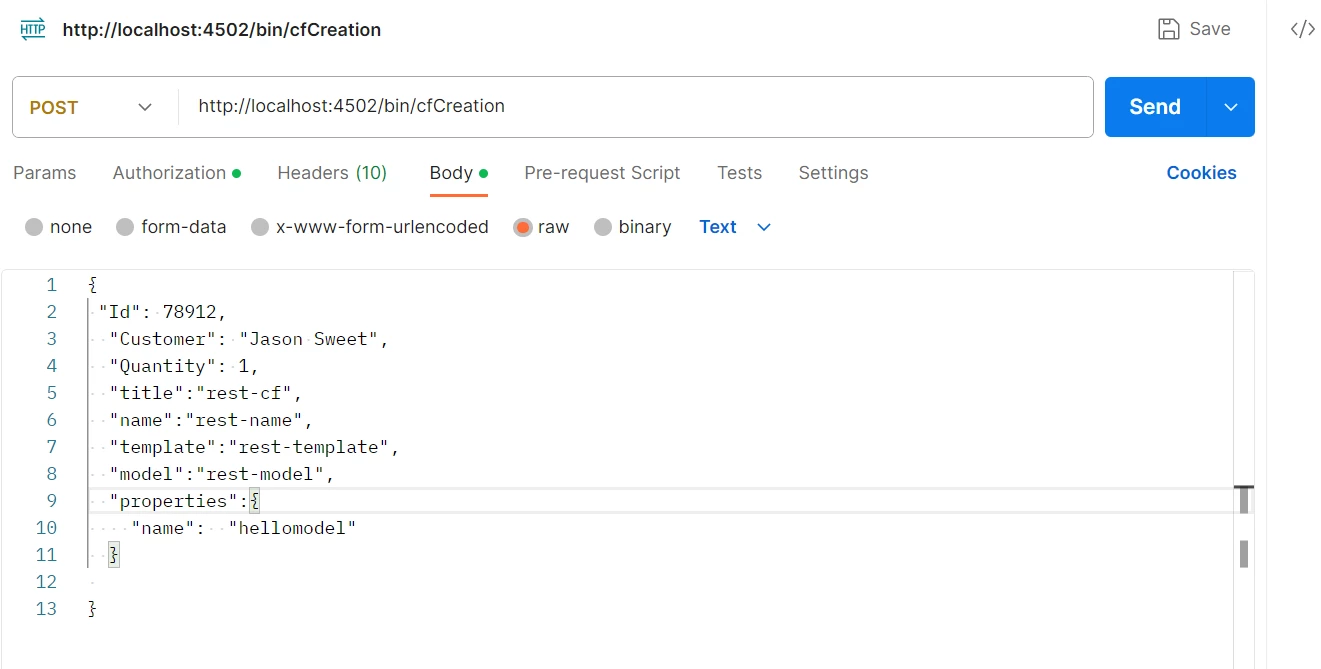
2. In the JSON body, you can send which model can be used , content properties, metadata .
contentModelPath : send as a JSON parameter as body.
3. Resource template = resolver.getResource(contentModelPath);
String contentModelPath = createParams.get("model");
Resource template = resolver.getResource(contentModelPath);
FragmentTemplate fragmentTemplate = getFragmentTemplate(template);
private FragmentTemplate getFragmentTemplate(Resource template) {
FragmentTemplate fragmentTemplate = template.adaptTo(FragmentTemplate.class);
if (null == fragmentTemplate) {
Resource jcrContentResource = template.getChild(JcrConstants.JCR_CONTENT);
if (null != jcrContentResource) {
fragmentTemplate = jcrContentResource.adaptTo(FragmentTemplate.class);
}
}
return fragmentTemplate;
}
3. FragmentTemplate.createTemplate(resource,name,title) will create the content fragment.
//cfLocation:under which path, it should create the content fragment
//you can send as JSON body paramter or create osgi config and get the content type location
Node path = JcrUtils.getOrCreateByPath(cfLocation, JcrResourceConstants.NT_SLING_FOLDER,
resolver.adaptTo(Session.class));
folderResource = resolver.getResource(path.getPath());
ContentFragment contentFragment = fragmentTemplate.createFragment(folderResource , name, title);
//name , title can send as paramters in JSON body request
4.
Once content fragment has been created , now update the metadata and content properties.
updateMetadata(contentFragment, metadata);
updateContentProperties(contentFragment, contentProperties, resolver);
private void updateMetadata(final ContentFragment contentFragment, JsonObject metadata) {
Iterator<Entry<String, JsonElement>> entrySet = metadata.entrySet().iterator();
entrySet.forEachRemaining(next -> {
try {
contentFragment.setMetaData(next.getKey(), next.getValue().getAsString());
} catch (ContentFragmentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
private void updateContentProperties(ContentFragment contentFragment, JsonObject, contentProperties,ResourceResolver resolver) throws Exception {
LOG.info("updateContentProperties:contentProperties::" + contentProperties);
Iterator<ElementTemplate> eleTemplates = contentFragment.getTemplate().getElements();
LOG.info("updateContentProperties eleTemplates" + eleTemplates);
while (eleTemplates.hasNext()) {
ElementTemplate nextEle = eleTemplates.next();
LOG.info("Processing NextEle - {}", nextEle.getName());
setElementValue(nextEle, contentFragment, contentProperties, resolver);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private void setElementValue(ElementTemplate nextEle, ContentFragment contentFragment, JsonObject contentObject,
ResourceResolver resolver) throws Exception {
if (null != contentObject && contentObject.has(nextEle.getName())) {
ContentElement contentElement = contentFragment.getElement(nextEle.getName());
FragmentData fragmentData = contentElement.getValue();
LOG.info("nextEle ::{}", nextEle.getName());
LOG.info("fragmentData Value::{}", fragmentData.getValue());
JsonElement propertyElement = contentObject.get(contentElement.getName());
String propertyValue = propertyElement.getAsString();
LOG.info("propertyValue:{}", propertyValue);
JsonArray arr = new JsonArray();
arr.add(propertyValue);
LOG.info("arr:{}", arr);
fragmentData.setValue(arr.get(0).getAsString());
if (null == contentElement) {
try {
contentElement = contentFragment.createElement(nextEle);
} catch (ContentFragmentException exc) {
LOG.error("Exception while setting element value: " + nextEle.getName(), exc);
throw new Exception("Failed to set element value: " + nextEle.getName());
}
}
contentElement.setValue(fragmentData);
}
}Q&A
Please use this thread to ask questions relating to this article

