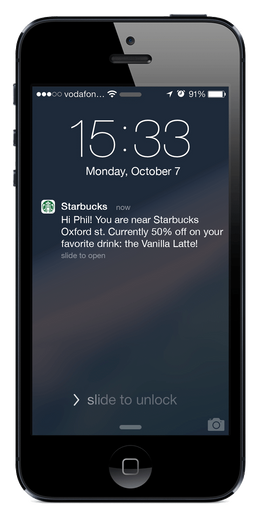
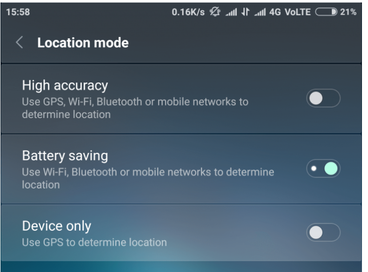
Latest Articles
Adobe Advertising Cloud Quick Tips #1
1.5K
3
2
Views
Likes
Replies
First-Party Data: Future of Digital Marketing
3.5K
7
5
Views
Likes
Replies
Creative Ways Digital Advertisers are Ruling the World! – Part 1
1.2K
0
0
Views
Likes
Replies
CTV- The new boon in storytelling
1.6K
0
0
Views
Likes
Replies
Performance Display Advertising - Best Practice for Brands/Advertisers
1.8K
3
0
Views
Likes
Replies
Understanding Programmatic Transactions in the Current Era of Digital Marketing
2.7K
1
1
Views
Like
Replies
Advertising in the times of Crisis
2.4K
5
0
Views
Likes
Replies
Demystifying Data #2: The Cuts Depend on the Dishes
2.9K
6
0
Views
Likes
Replies
The Untapped Potential of Audio Advertising
6.3K
5
2
Views
Likes
Replies
Stalled Auto industry now eyeing towards Video Advertising to keep the Engine running
6.4K
6
2
Views
Likes
Replies